Tag: Oracle
In Oracle PL/SQL, the COUNT method is a function that returns the number of items in a collection (ignoring the deleted items even if DELETE stores fillers for them). Syntax of COUNT collection...
In Oracle PL/SQL the FIRST and LAST methods are functions. If there is at least one element in the collection, FIRST and LAST return the indexes of the first and last element respectively...
In Oracle PL/SQL, the EXISTS method is a function that tells you if a specified Varray or Nested Tables element exists. Syntax of the EXISTS method in Oracle PL/SQL collection_name.EXISTS...
In Oracle PL/SQL, the EXTEND method is a procedure that adds elements to the end of Varray or Nested Tables. The collection can be empty, but not NULL. Syntax of EXTEND method in Oracle...
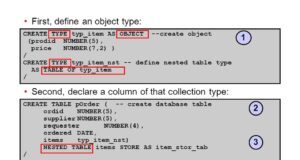
In Oracle PL/SQL Nested Tables is a column type that stores an unlimited row set in a certain order.When you extract a nested table value from a database into a Nested Tables...
In Oracle PL/SQL Varray (an array with variable size) is an array whose number of elements can vary from zero (empty) to the declared maximum size.To access a Varray element, use the...
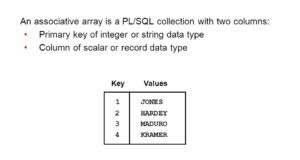
In Oracle PL/SQL Associative Arrays, also known as index tables, which use arbitrary numbers and rows for index values.Associative Arrays is a set of key-value pairs where each key is unique...
In Oracle PL/SQL, the %TYPE attribute for a variable provides the database column data type. This is especially useful when declaring variables that will contain the values of the database table...
In Oracle PL/SQL, the %ROWTYPE attribute provides a record type representing a string in the Oracle database table (or view).A record may store an entire string of data selected from the...
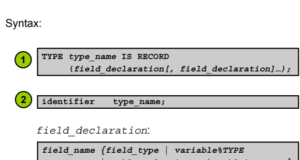
Record type is a group of linked data elements stored in fields, each with its own name and data type. You can use Record as a variable, which may contain a table row or some columns (fields)...
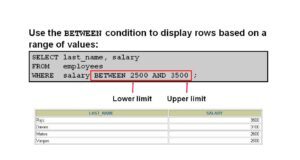
Oracle BETWEEN condition (also called BETWEEN operator) is used to obtain values within a range in SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE sentences. Syntax of BETWEEN condition in...
Oracle IS NOT NULL condition is used to check for the value NOT NULL. You can use the Oracle condition IS NOT NULL either in an SQL sentence or in a block of PLSQL code. Syntax for IS NOT...
The Oracle IS NULL condition is used to check the NULL value. You can use the IS NULL condition either in an SQL sentence or in a block of PLSQL code. Syntax for IS NULL condition in...
The Oracle IN condition (also called the IN operator) determines whether a value or a list of values corresponds to an expression in the specified resulting SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE...
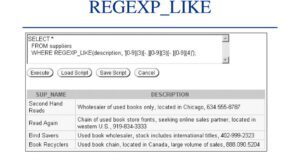
Oracle condition REGEXP_LIKE allows to execute regular expressions in WHERE proposal in SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE queries. Syntax for REGEXP_LIKE in Oracle/PLSQL REGEXP_LIKE (...
Oracle condition LIKE allows to use wildcards which will be used in WHERE operator in SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE queries. This allows comparison with a pattern. LIKE syntax in...